equities | july 20, 2023
Where Now for Global Equity Markets?
Five forces defining the equity cycle.
Key Insights
Equity markets are already focusing on when monetary tightening will be reversed. History suggests this will only occur when inflation falls sustainably below interest rate levels.
With the era of stimulus behind us, equity return patterns are likely to differ from the past. This implies the need for breadth, and at times, a contrarian approach.
Finding companies able to withstand margin pressures and maintain earnings growth through the next stage of the equity cycle will likely be rewarded.

Scott Berg
Portfolio Manager, Global Growth Stock Fund
Equity markets have performed well this year, but much of the gains have been concentrated in U.S. mega‑cap technology stocks. Meanwhile, the U.S. Federal Reserve (Fed) appears determined to stay the course until inflation shows real signs of decline. With the complexity of equity markets reaching new heights, investors are having to deal with a series of extremes that are both unusual, but highly influential. Below, we address five forces that will be key in shaping the next stage of the equity cycle.
Subscribe to T. Rowe Price Insights
Receive monthly retirement guidance, financial planning tips, and market updates straight to your inbox.
Five Forces Defining the Global Equity Cycle
Investors are having to deal with a series of extremes

For illustrative purposes only.
Source: T. Rowe Price.
1. The End of Stimulus
With the U.S. Federal Reserve and other central banks tightening monetary supply (Figure 1) to deal with the inflationary hangover of the coronavirus pandemic, it is extremely unlikely that we will return to a stimulus‑driven world, given the clear risks posed by rising prices. This matters because stimulus has played such a large part in raising asset prices over the past decade. It also matters because the market is anticipating material interest rate cuts as we move into 2024.
The challenge for central banks is playing out via recent equity market strength. Despite the Fed aggressively trying to suppress inflationary pressures through the removal of stimulus and one of the fastest rate hike cycles in history, there is so much money in the global economy that there remains ample liquidity to create asset price inflation. The level of policy aggression has set the scene for risk events to emerge, such as the recent U.S. banking collapses. But, despite a decelerating economy and worries over credit risk, we have seen investor bullishness replace extreme bearishness in a very short space of time. Regardless of the risks of rapid liquidity withdrawal, the Fed appears committed to deflating the economy. Its ability to manage inflation down in a smooth fashion may be tested in the next stage of the cycle, however.
 Equity markets have performed well this year, but much of the gains have been concentrated in U.S. mega‑cap technology stocks.
Equity markets have performed well this year, but much of the gains have been concentrated in U.S. mega‑cap technology stocks. 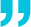
Dramatic Decrease in Stimulus
(Fig. 1) Stimulus is back on a downward path after the recent U.S. banking crisis
As of May 31, 2023.
*Global stimulus is the amount of fiscal stimulus in the financial system generated by world central banks.
Global Assets Impulse = Global central bank and fiscal liquidity injections divided by the Total size of global financial markets. There is no guarantee that any forecasts made will come to pass. Actual results may vary.
Sources: Bloomberg Index Services Limited. Bloomberg Finance L.P. U.S. Federal Reserve, U.S. Department of the Treasury, European Central Bank, Bank of Japan, and Bank of International Settlements. Data analysis by T. Rowe Price.
2. Economic Deceleration and a Hard or Soft Landing
One unusual feature in this market cycle has been the lack of synchronicity. Monetary policy tightening “normally” forces a deceleration in investment, spending, and hiring in unison, with the overall effect being broad‑based deflation. However, in this cycle, wages have continued to rise and consumption trends have remained solid, even as the economy decelerates.
Separately, we haven’t seen any meaningful credit cycle, and while there are some small signs that unemployment is on the rise, corporate sentiment remains relatively robust given the strength of balance sheets entering the tightening cycle.
This means we have a labor market that is remarkably tight, despite the Fed trying to induce higher unemployment. This lack of synchronicity is partly the reason why the U.S. economy is faring so well in the face of such aggressive monetary tightening. But this may mean more inflation—or at least more sticky inflation—as we move through the coming quarters.
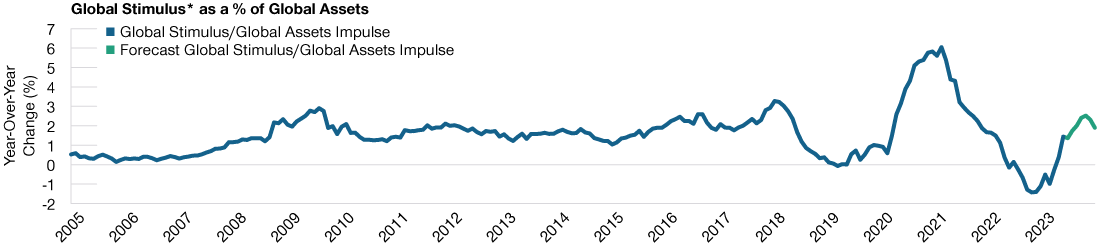
While the consequences of driving down inflation will potentially lead to lower economic growth (Figure 2), this has clearly become the Fed’s most favored option when choosing between the “rock” and the “hard place.” However, the softness at which the landing is taking place, thus far, is acting as a soother for equity markets.
Will We Have a Soft or Hard Economic Landing?
(Fig. 2) U.S. economic growth is fading
As of May 31, 2023.
Sources: Institute for Supply Management/Haver Analytics and J.P. Morgan/IHS Markit (see Additional Disclosure).
3. Deglobalization and the China‑U.S. Decoupling
The era of peak market liberalization and globalization is now firmly behind us, with consequences for productivity, inflation, and economic redistribution in the coming decade. What has become clear in recent years is how the U.S. and China are decoupling on economic and political levels. This implies more domestic investment as both parties try to build independent supply chains that were previously interlinked. This will take time, but the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act will help to incentivize domestic investment, helping to create more independence from China.
However, the U.S. cannot decouple immediately given the time horizon to build capability and because unemployment remains so low in the U.S., creating a challenge of capacity and inflation management. But we believe the U.S. government is serious about building the required infrastructure to create independence from China, and that is why being on the right side of this change at a stock‑specific level will be important.
Our view on China remains that the market is investible, but that selectivity will be key given the shift toward more centralized policymaking. Greater political intervention implies a changed environment both for investment flows and for the freedom of wealth creation. This will undoubtedly influence risk premia.1
 While the consequences of driving down inflation will potentially lead to lower economic growth, this has clearly become the Fed’s most favored option....
While the consequences of driving down inflation will potentially lead to lower economic growth, this has clearly become the Fed’s most favored option.... 
4. Artificial Intelligence and Being on the Right Side of the Investment Cycle
No investment perspective is complete without reference to artificial intelligence (AI), especially how influential the theme has been for equity markets so far this year. We believe we are only in the early stages of an investment cycle, with recent quarterly results from companies like NVIDIA indicating that AI is attracting large‑scale investment as well as competition for investment. This brings tremendous opportunity, but also thought regarding the durability and valuation for those investing and benefiting from this investment cycle.
Uses for AI are broad‑based, with its influence spanning software development, semiconductor and data center enablement, and cybersecurity in information technology to name but a few. Education, media development, fuel efficiency, fintech and financial data provision, and medicine are all potential sources of impact for AI, based on a world where more data is now created per hour than in an entire year two decades ago, but where only 1% of global data is captured, stored, and used. AI is set to change this capture rate dramatically.
What is clear, however, is that it will be important to position for the right side of the AI cycle, given the magnitude of spending occurring at a time when many corporate margins are compressing. This is a short‑term consideration with longer‑term analysis centering on which businesses may be disrupted or adopted en masse as user experience rapidly changes.
While this theme will be long‑lived and evolutionary, we are comfortable with our exposure, which is currently centered on the enablers of AI, where ongoing cyclical pressures in traditional business lines create opportunities to access AI‑driven growth at reasonable valuations.
 [AI] brings tremendous opportunity, but also thought regarding the durability and valuation for those investing and benefiting from this investment cycle.
[AI] brings tremendous opportunity, but also thought regarding the durability and valuation for those investing and benefiting from this investment cycle. 
5. End of the Goldilocks Era for Corporate Profits
The above forces are symptomatic of an unusual cycle where the echoes of the global financial crisis (GFC) are still present. Rapid technological change, COVID, and geopolitical conflict are creating the setup for a bumpy ride going forward, where grinding out returns will be important. We believe markets will increasingly reward those companies that can withstand an economic decline and maintain or expand profit margins.
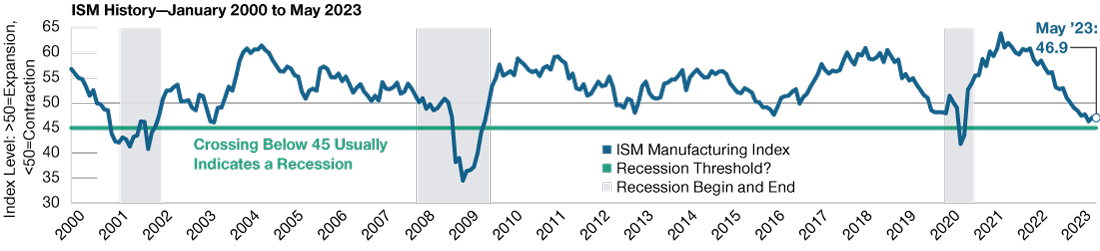
With the era of low interest rates, low taxes, low wage growth, cheap commodity prices, easy technological gains, and deflationary globalization now passed, this will have implications for profit margins for all companies (Figure 3). While the first half of 2023 has somewhat hidden this theme, as mega‑cap technology companies have exerted a strong influence on equity returns, this narrowness will inevitably fade to create greater market breadth.
New Environment Has Implications for Company Earnings
(Fig. 3) Corporate earnings expectations are falling sharply
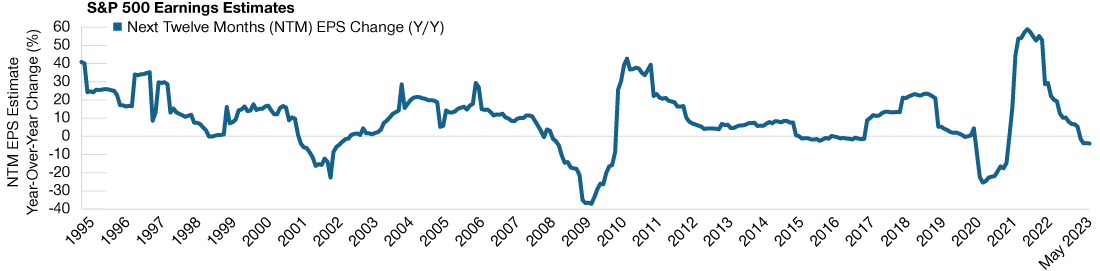
As of May 31, 2023.
For illustrative purposes only. There can be no assurance that the estimates will be achieved or sustained. Actual results may vary.
Sources: J.P. Morgan/IHS Markit, and Bloomberg Finance L.P. (see Additional Disclosure). Data analysis by T. Rowe Price.
Finding the Best Way Forward
While the past three years have been dominated by the swinging pendulum between growth and value stocks, we believe the future implies more of a focus on stock specifics and on companies that can grow and compound their earnings through a fundamentally changed cycle. We believe the era of stimulus, consistently expanding multiples, and a repeat of post‑GFC equity return patterns are largely behind us. This implies breadth in portfolios and risk management and the readiness to increase equity exposure when risk events happen and when contrarian opportunities present themselves. Our job is to identify which companies will thrive through the next stages of the equity cycle.
 …the future implies more of a focus on stock specifics and on companies that can grow and compound their earnings through a fundamentally changed cycle.
…the future implies more of a focus on stock specifics and on companies that can grow and compound their earnings through a fundamentally changed cycle. 
The weight of NVIDIA in the Global Growth Stock Fund as of June 30, 2023 was 2.1%.
Call 1-800-225-5132 to request a prospectus or summary prospectus; each includes investment objectives, risks, fees, expenses, and other information you should read and consider carefully before investing.
1Expected compensation for taking on additional risk.
Additional Disclosure
Information has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable but J.P. Morgan does not warrant its completeness or accuracy. The index is used with permission. The Index may not be copied, used, or distributed without J.P. Morgan’s prior written approval. Copyright © 2023, J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. All rights reserved.
Important Information
This material is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended to be investment advice or a recommendation to take any particular investment action.
The views contained herein are those of the authors as of July 2023 and are subject to change without notice; these views may differ from those of other T. Rowe Price associates.
This information is not intended to reflect a current or past recommendation concerning investments, investment strategies, or account types, advice of any kind, or a solicitation of an offer to buy or sell any securities or investment services. The opinions and commentary provided do not take into account the investment objectives or financial situation of any particular investor or class of investor. Please consider your own circumstances before making an investment decision.
Information contained herein is based upon sources we consider to be reliable; we do not, however, guarantee its accuracy. Actual future outcomes may differ materially from any estimates or forward‑looking statements provided.
Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance. All investments are subject to market risk, including the possible loss of principal. Growth stocks are subject to the volatility inherent in common stock investing, and their share price may fluctuate more than that of a income‑oriented stocks. Investing in technology stocks entails specific risks, including the potential for wide variations in performance and usually wide price swings, up and down. Technology companies can be affected by, among other things, intense competition, government regulation, earnings disappointments, dependency on patent protection and rapid obsolescence of products and services due to technological innovations or changing consumer preferences. International investments can be riskier than U.S. investments due to the adverse effects of currency exchange rates, differences in market structure and liquidity, as well as specific country, regional, and economic developments. These risks are generally greater for investments in emerging markets. All charts and tables are shown for illustrative purposes only.
202307-2975026
Next Steps
Get strategies and tips for today’s market conditions.
Contact a Financial Consultant at 1-800-401-1819.